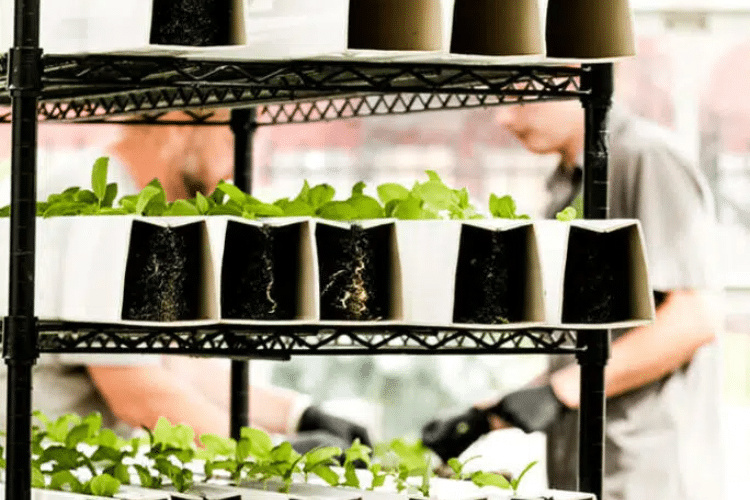
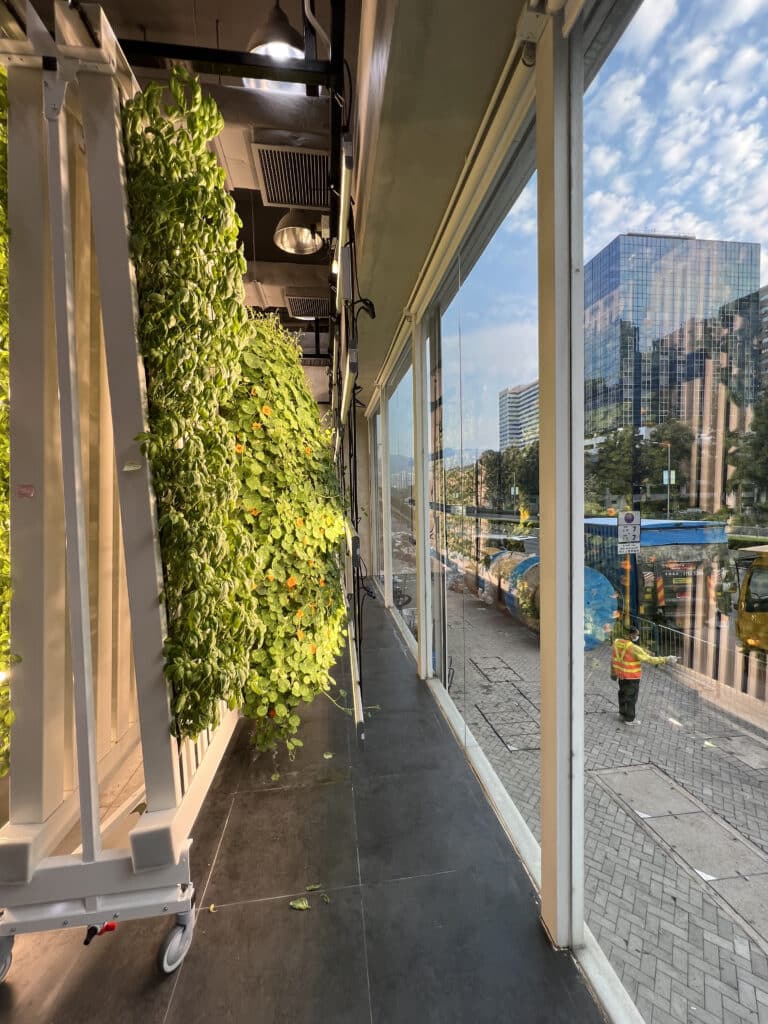
Image @Agrician in Hong Kong and their urban ZipFarm build
Urban farming has emerged as a viable solution to grow fresh produce within cities. If you’re enthusiastic about starting your own urban farm, there are several things you need to consider before you get growing.
In this blog post, we’re going over considerations for urban farming business focusing on a custom ZipFarm™ or ZipPod container farm, and other factors that should be top of mind that can help you to turn your green dream into a thriving reality.
Container v’s custom farm
At ZipGrow, we provide various solutions for small businesses through to large commercial-scale operations. Depending on what your business plan needs are, how much you want to scale, and your budget should dictate if you are looking for a custom-built farm within a given space or a container farm that needs a space to land.
In a nutshell, a container farm, like a ZipPod, pairs perfectly with a business plan that serves a smaller, more defined cap on production needs for those with limited space and communities that require quick access to food production systems. As long as you have access to a water supply and 200 amp electrical service, a ZipPod can start growing the moment you take possession. From the desert plaines to the frigid North, it’s also perfect for areas with extreme climates.
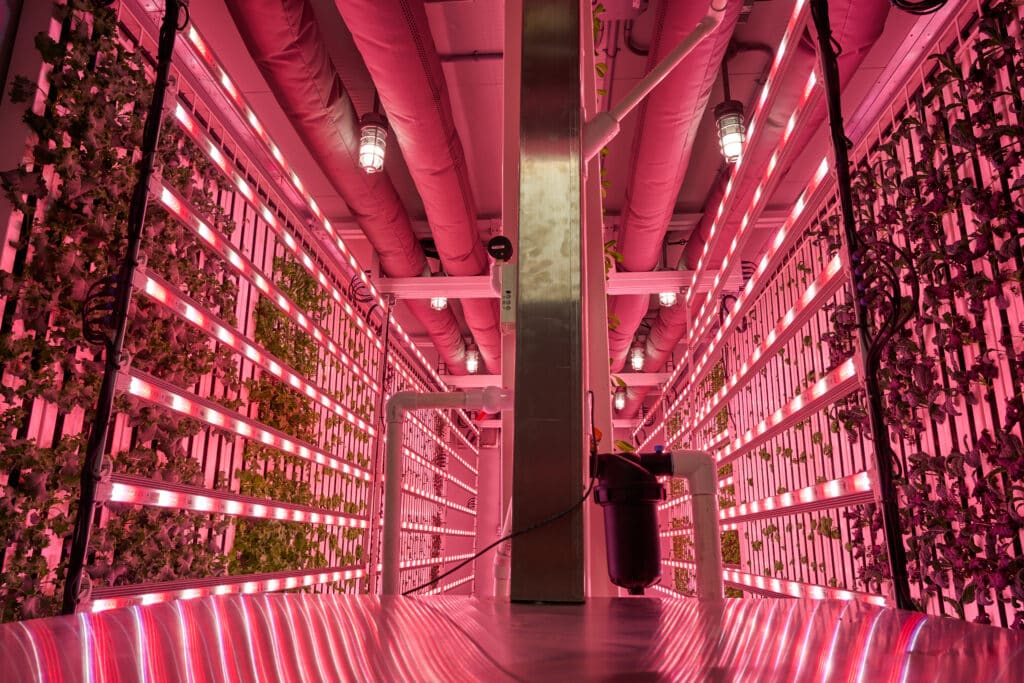

The portability of a container farm allows for quick expansion and deployment of your farming operation while limiting the overhead costs of warehouse development and leasing.
Learn why a purpose-built container farm may be a good fit for you. A ZipFarm, on the other hand, will take several months of preparation on your part before you sow a single seed; however, the long-term benefits of customizing your own space can be worth the wait. You can tailor the farm to your future goals. A ZipFarm™ is scalable and allows for the addition of offices, packaging, and storage areas and greater control over workable spaces.
Sourcing a space and site
Siting your farm is the process of choosing a location for your growing facilities. Many factors go into choosing a location, including things like real estate cost, access to markets and suppliers, neighboring communities and business, and the state of the site itself. Also, think about the environment you will want for the end product of your vision.
Assess the available indoor spaces, such as warehouses, empty buildings, or repurposed structures. Consider factors like floor space, ceiling height, and structural integrity to accommodate your ZipGrow™ system and plants.
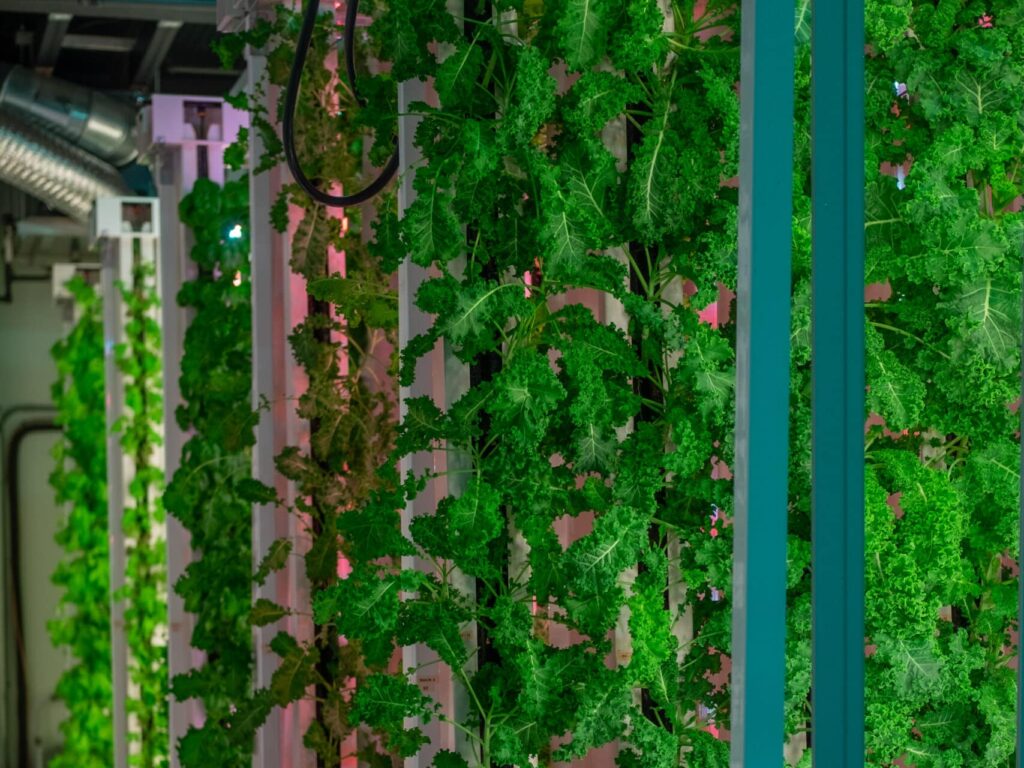

Strip malls and warehouses are popular and middle units are ideal, as the side walls will be better insulated. For a ZipFarm™, the minimum size for the growing room would be 25 feet wide with a ceiling height of 12-14 feet. You want to make sure that your environmental conditions are on point. External walls need an insulation rating of R22 or higher, and the walls will require a vapor barrier of paint or plastic/metal barrier.
Once you find a suitable space, the ZipGrow engineering team can assess if it is viable and help you to determine what customizations are required before they professionally install the farm.
Zoning and regulation
Here's what you need to know:
Research Local Laws
Mixed-Use or Commercial Zones

Check Permitted Activities
Obtain Necessary Permits

Engage with Local Authorities
Compliance with Building Codes
Waste Management
Expertise and Training